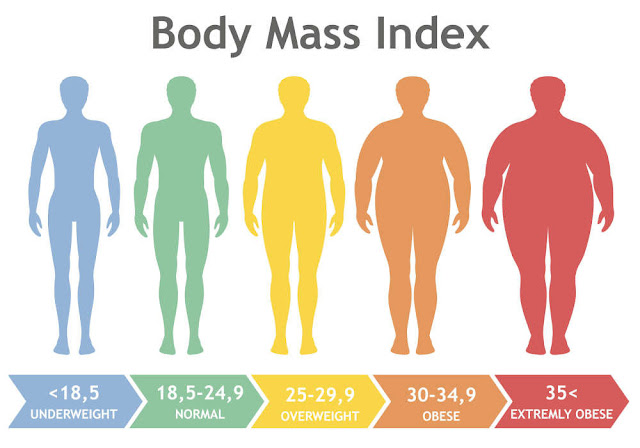
The World Health Organization defines obesity and overweight as abnormal and excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health. The most commonly index used in classifying overweight or obesity in adults is the body mass index (BMI). This is weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters (kg/m2). A BMI equal to or greater than 25 is classified overweight, and that which is equal to or greater than 30 is classified obese.
Obesity usually results from
consuming more calories than the quantity spent. When a person consumes more energy dense
foods without an equivalent increase in energy expenditure (physical activity),
weight gain follows. Also, a decrease in the amount of physical activity
without a decrease in calories consumed will result in weight gain. Here are
some interesting facts about obesity:
1. Obesity and being
overweight in general predisposes a person to noncommunicable diseases like
type 2 diabetes; cancers like endometrial, colon, kidney, breast, ovarian,
liver, prostate and gallbladder; musculoskeletal disorders like osteoarthritis;
and cardiovascular diseases (especially heart disease and stroke).
2. Adopting a healthy
lifestyle is a person's best bet against obesity. A healthy lifestyle basically
consists of eating healthy and engaging in regular physical activity. Calorie
intake from fats and sugars should be limited, while the consumption of fruits,
vegetables, lean meats and legumes is increased. Adults should engage in a
minimum of 150 minutes of physical activity per week. Other elements of a
healthy lifestyle are stress management and maintaining a regular sleep
pattern. The National Sleep Association recommends 7 to 9 hours of sleep per
night for adults.
3. Certain
medications are known to cause weight gain, which could lead to overweight or
obesity. These include:
- Most corticosteroids such as prednisone, bethamethasone, diprosone, methylprednisolone and dexamethasone;
- Some high blood pressure medications, such as metoprolol, atenolol;
- Some diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones;
- Some anticonvulsants, such as Tegretol, Carbatol and Depakene;
- Some antidepressants, such as paroxetine, sertraline, fluoxetine and citalopram;
- Some oral contraceptives (hormonal contraceptives).
4. Some diseases
contribute to obesity. These include: insulin resistance, hypothyroidism,
polycystic ovarian syndrome, and Cushing's syndrome. Some people with
depression overeat, which can lead to excessive weight gain and ultimately,
obesity.
5. Science has proven
that genes affect obesity as well. Genes can directly cause obesity in specific
disorders, including Bardet-Biedl syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome.

Comments
Post a Comment